Diarrhoea and vomiting
Feeling sick and then vomiting is usually the first sign that your child has a ‘tummy bug’. Diarrhoea tends to occur after your child has started vomiting and means passing frequent watery poos that are offensive in nature.
- Tummy bugs are extremely common in young children and are almost always caused by a virus. They are easily spread, resulting in outbreaks in nurseries and schools
- Babies under 1 year of age (and especially under 6 months of age) are at more risk of becoming dehydrated when they have a tummy bug than older children, which is why it is important to make sure that they are drinking enough
Operation Ouch - Diarrhoea and vomiting
When should you worry?
If your child has any of the following:
- Has dark green or blood stained vomit
- Breathing very fast, too breathless to talk, eat or drink
- Working hard to breathe, drawing in of the muscles below the ribs, or noisy breathing (grunting)
- Breathing that stops or pauses
- Is pale, blue, mottled or feels unusually cold to touch
- Difficult to wake up, very sleepy or confused
- Weak, high-pitched cry or can’t be settled
- Has a fit (seizure)
- Has a rash that does not disappear with pressure (the ‘Glass Test’)
- Is under 3 months old with temperature more than 38°C or under 36°C (unless fever in the 48 hours following vaccinations and no other red or amber features
You need urgent help
Please phone 999 or go to the nearest Hospital Emergency (A&E) Department.
If your child has any of the following:
- Has blood in their poo or wee
- Has tummy pain that doesn’t go away for more than 1 day even after paracetamol or ibuprofen
- Is vomiting and unable to keep down any fluids
- Is drinking or breastfeeding much less than normal
- Breathing a bit faster than normal or working a bit harder to breathe
- Dry skin, lips or tongue
- Not had a wee or wet nappy in last 8 hours
- Poor feeding in babies (less than half of their usual amount)
- Irritable (Unable to settle them with toys, TV, food or hugs even after their fever has come down)
- Is 3-6 months old with temperature 39°C or above (unless fever in the 48 hours following vaccinations and no other red or amber features)
- Temperature of 38°C or above for more than 5 days or shivering with fever (rigors)
- Temperature less than 36°C in those over 3 months
- Getting worse and I am still worried
You need to contact a doctor or nurse today
Please ring your GP surgery or contact NHS 111 - dial 111 or for children aged 5 years and above visit 111.nhs.uk
- Watch them closely for any change and look out for any red or amber symptoms
- Additional advice is also available for families for help cope with crying in otherwise well babies
- If your child has a long term condition or disability and you are worried please contact your regular team or follow any plans that they have given you.
Self care
Using the advice below you can provide the care your child needs at home.
What should you do?
- Avoiding dehydration is important – give your baby/child extra fluids. Give your baby oral rehydration solution (ORS) in between feeds or after each watery stool. Little and often tends to work best – in hospital, babies are given 1 or 2 tablespoons (5-10 mls) of fluid to drink every 5-10 minutes. You can try using a syringe to give fluids to your child. Mixing the contents of the ORS sachet in dilute squash (not “sugar-free” squash) instead of water may improve the taste
- Do not stop giving your baby milk. If you are breastfeeding, continue doing so and offer the breast more frequently
- Do not worry if your child is not interested in solid food. If they are hungry, offer them plain food such as biscuits, bread, pasta or rice. It is advisable not to give them fizzy drinks as this can make diarrhoea worse
- To avoid spreading the virus, wash your hands with soap and water after changing nappies. Keep toilets clean and don’t share towels
- They should not return to school or any other childcare facility until 48 hours after the last episode of diarrhoea and / or vomiting
- You can get Oral Rehydration Solution from the pharmacy
How long will your child’s symptoms last?
- Vomiting tends to last for 1-2 days, and diarrhoea tends to last for about 5 days
- The charts below show how long diarrhoea and vomiting lasts in children when they have a tummy bug. The faces represent 10 children who have seen their GP with a tummy bug. Green faces are those children who have recovered within that time period
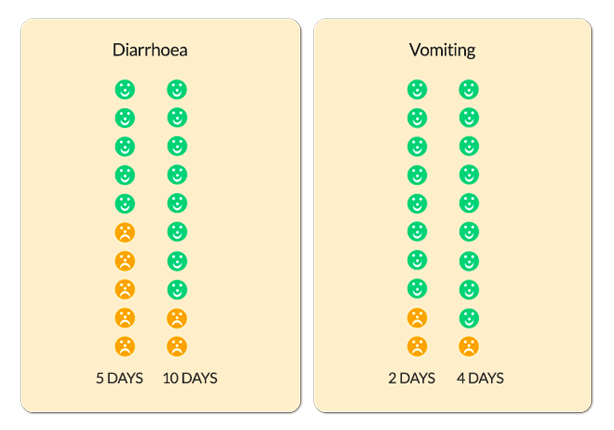
The diagrams above are taken from www.whenshouldiworry.com
Where should you seek help?
- If it is non-urgent, speak to your local pharmacist or health visitor.
- If your child has any of the above features, urgently see your GP. For an urgent out-of-hours GP appointment, visit NHS 111 Online or for children under 5 call 111
- You should only call 999 or go to your nearest A&E department in critical or life threatening situations.
Health visitors are nurses or midwives who are passionate about promoting healthy lifestyles and preventing illness through the delivery of the Healthy Child Programme. They work with you through your pregnancy up until your child is ready to start school.
Health Visitors can also make referrals for you to other health professionals for example hearing or vision concerns or to the Community Paediatricians or to the child and adolescent mental health services.
Contact them by phoning your Health Visitor Team or local Children’s Centre.
Sound advice
Health visitors also provide advice, support and guidance in caring for your child, including:
- Breastfeeding, weaning and healthy eating
- Exercise, hygiene and safety
- Your child’s growth and development
- Emotional health and wellbeing, including postnatal depression
- Safety in the home
- Stopping smoking
- Contraception and sexual health
- Sleep and behaviour management (including temper tantrums!)
- Toilet training
- Minor illnesses
For more information watch the video: What does a health visitor do?
School nurses care for children and young people, aged 5-19, and their families, to ensure their health needs are supported within their school and community. They work closely with education staff and other agencies to support parents, carers and the children and young people, with physical and/or emotional health needs.
Primary and secondary schools have an allocated school nurse – telephone your child’s school to ask for the contact details of your named school nurse.
There is also a specialist nurse who works with families who choose to educate their children at home.
Sound Advice
Before your child starts school your health visitor will meet with the school nursing team to transfer their care to the school nursing service. The school nursing team consists of a school nursing lead, specialist public health practitioners and school health staff nurses.
They all have a role in preventing disease and promoting health and wellbeing, by:-
- encouraging healthier lifestyles
- offering immunisations
- giving information, advice and support to children, young people and their families
- supporting children with complex health needs
Each member of the team has links with many other professionals who also work with children including community paediatricians, child and adolescent mental health teams, health visitors and speech and language therapists. The school health nursing service also forms part of the multi-agency services for children, young people and families where there are child protection or safeguarding issues.



